
OPC UA realtime streaming in Grafana: Part 2
Welcome to the second installment of our series, where we’ll develop a Grafana plugin capable of streaming realtime data from any OPC Unified Architecture (OPC UA) server. In my prior projects, I’ve handled data collection from various IoT devices using the OPC UA client/server framework for seamless data exchange between devices and applications and there was a need for direct integration between Grafana and OPC UA streaming.
What we will cover in Part 2
In part1 we’ve covered how to setup the development environment needed to develop our Grafana plugin. Additionally, we’ll successfully started a local Grafana instance running inside a Docker container. In this part of the series I will explain the basic structure of our Grafana Plugin.
Plugin architecture
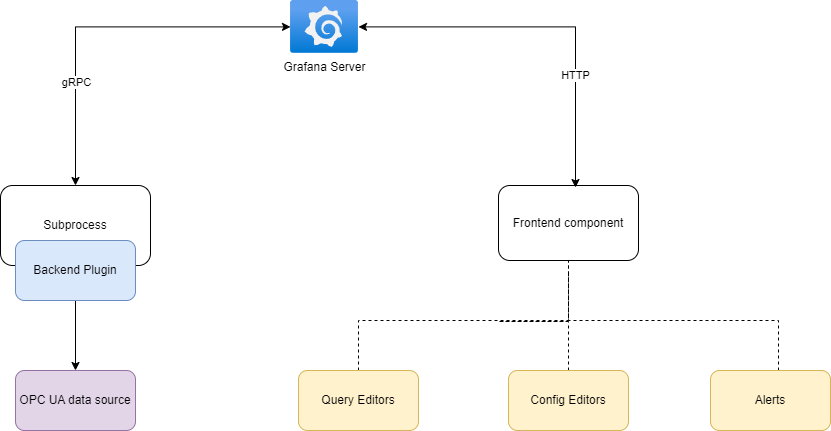
Our Grafana plugin consists of two components: A backend and a frontend.
In Grafana, backend plugins and frontend components are not within the same subprocess. Let’s break it down.
Backend Plugins:
- Backend plugins run as separate subprocesses launched by the Grafana server.
- They handle tasks like querying data from data sources, managing resources, and performing health checks.
- Communication with backend plugins occurs over gRPC (Google’s Remote Procedure Call protocol).
Frontend Components:
- Frontend components (such as panels, query editors, and visualizations) run in the user’s browser.
- They interact with the Grafana server via HTTP requests.
- When a frontend component needs data, it sends a request to the Grafana server, which then communicates with the relevant backend plugin.
- The backend plugin processes the request and responds to the Grafana server, which forwards the data back to the frontend.
Summary:
- Backend and frontend communicate indirectly through the Grafana server, ensuring stability and security.
- This separation allows Grafana to integrate with various services while maintaining a robust architecture.
Now that we have a clear understanding of the overall plugin architecture, let’s look at the functionalities of the backend and frontend components.
Backend component
The backend component of our plugin is written in Go and uses the Grafana plugin SDK for Go. It exeuctes in a subprocess launched by the Grafana server. Communication between the backend component and Grafana server is over gRPC.
Its primary responsibility is to stream data from OPC UA data sources to the frontend component. It handles secure connections to the OPC UA data sources and provides functionalities for browsing and subscribing to OPC UA nodes.
It will support the following functionality:
- Connection to OPC UA data sources
- Authentication:
- Anonymous - anynomous authentication, no username and password needed
- Username and password - authentication using username and password
- Security policy:
- None - No security policy
- Basic128Rsa15 - Encryption using RSA 128-bit and SHA1 for signing requests
- Basic256 - Encryption using AES 256-bit and SHA-1 or SHA-256 for signing requests
- Basic256Sha256 - Encryption using AES 256-bit and SHA-256 for signing requests
- Security mode:
- Sign - requests are signed but not encrypted
- SignAndEncrypt - requests are signed and encrypted
- None - requests are sent as-is without signing or encryption
- Authentication:
- Client certificates - manages client certificates generation automatically.
- Browse OPC UA nodes - handles browsing nodes in OPC UA data sources
- Subscribe to OPC UA nodes - handles subscription to OPC UA nodes
- Alerting - handles alerting
Frontend component
The frontend component is written in Typescript using the React framework and runs in the user’s browser, hosted by the Grafana server.
Its primary responsibility is to enable users to configure OPC UA data sources to connect to, and subscribe to OPC UA nodes for streaming. Additionally it enables users to set up alerting rules for the subscribed OPC UA nodes.
It communicates with the backend via HTTP API calls to the Grafana server, which in turn forwards the message over gRPC to the backend component.
Conclusion
In this segment of our series, we’ve covered the basic architecture of our Grafna plugin and how it consists of a backend and frontend component. We’ve also explained the functionalities of the backend and frontend component.
This concludes Part 2 of our series. In part3, I’ll guide you through the impementation of the backend component.